In statistics, the term bias is used in two different ways
- A biased sample is a statistical sample where their members have not the same probability to be chosen.
- A biased estimator is one estimator that over or understimates the quantity to be estimated.
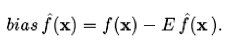 reflecting sensivity to the target function f(x). The bias represents "how closely on average the estimate is able to approximate the target". The bias has direct effects on the predicted error as we can decompose it as follows [2]
reflecting sensivity to the target function f(x). The bias represents "how closely on average the estimate is able to approximate the target". The bias has direct effects on the predicted error as we can decompose it as follows [2]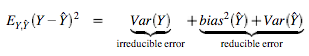
References
[1] J. H. Friedman, "On bias, variance, 0/1 loss, and the curse-of-dimensionality", Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery vol.1, nº 1, 55-77, 1997. (Download).
[2] G. M. James, "Variance and Bias for General Loss Functions", Machine Learning 51, nº 2, 115-135, 2003. (Download)










0 comments:
Post a Comment